Concepts in science
Plant Cuticle
Cuticle: a hydrophobic boundary layer that coats the outer face of the epidermis of aerial plant organs.
Suberin: a hydrophobic polyester deposited in the apoplast of endodermal and peridermal cells, abscission zones, scar tissues, and seed coats.
Cutin: a polyester network of predominantly fatty acids that constitutes a major component of the plant cuticle.
Cross-link: a lateral covalent linkage between two polymer chains.
Long-chain fatty acid: a fatty acid that is 16 or 18 carbons in length.
Depolymerization: the breakdown of a polymer into its constituent monomers.
Gas chromatography: an analytical technique to separate and quantify the abundance of compounds that are volatile in a gaseous phase.
Apoplast: the continuous region throughout the plant that is external to the plasma membranes.
Dendrimer: a branching, tree-like structure with a single origin and many termini.
Monoacylglycerol: a molecule consisting of glycerol ester-linked to a single acyl chain.
Magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS NMR): a method of solid-state NMR spectroscopy that gives improved peak resolution.
Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase (LACS) proteins: enzymes that conjugate a molecule of coenzyme A to the carboxyl end of a fatty acid.
Cytochrome P450: a large family of enzymes that typically perform oxidation reactions.
Cutinase: an enzyme that hydrolyzes polymeric cutin polymers, breaking the ester linkages.
Epidermal-growth-control theory: the thory that turgor-driven organ growth is constrained by the rigid epidermal layer.
Mass spectrometry or chromatography
原子量Atomic mass: Relative atomic mass, 原子量的单位为道尔顿Da。而1道尔顿的定义为C12原子静止质量的1/12. 原子核的质子和中子几乎占原子总质量的全部。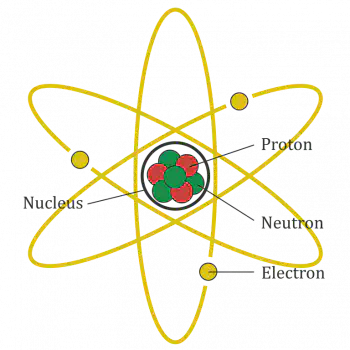
同位素isotope:含有相同的质子数不同中子数的原子。包括放射性同位素和稳定同位素。比如C13 和O18就属于稳定同位素。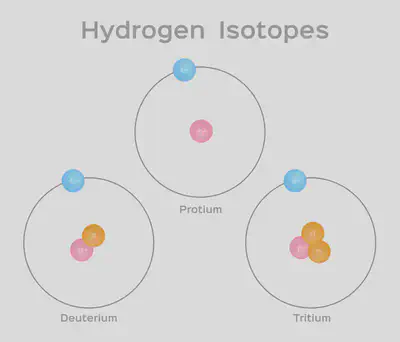
同位素丰度isotope abundance/Natural abundance:自然界中存在的某一元素的各种同位素的相对含量,比例是固定的。比如在地球上,氧的同位素丰度:16O=99.76%,17O=0.04%,18O=0.20% 
平均质量(average mass ):计算时候,每个同位素质量都要乘以丰度,然后加和。比如氧气(O2)的平均分子量: 2*(15.994915*99.76%+16.999131*0.038%+17.999159*0.2%)这里需要说明,大家日常所叫的分子量(molecular weight),大多数时候便是平均质量。
精确质量 (Exact mass):是以丰度最高的同位素质量进行直接进行加和得到。

质谱正负离子模式的选择:物质需要离子化后也就是需要带电才能被质谱检测。主要根据化合物的性质,也就是看结构的不同,有些物质在电离时容易带正电荷,有些容易带负电荷。
- 正离子模式:适合碱性样品,如还有赖氨酸、精氨酸和组氨酸等肽类。可用乙酸(pH=3-4)或者甲酸(pH=2-3)对样品进行酸化。如果样品pK值已知,则pH至少要低于pK值2个单位。 碱性化合物容易加合质子,带正电荷,形成[M+H]+,m/z会多H的分子量。此外,还有其他带正电的加合物,[M+Na]+,[M+K]+,[M+NH4]+。
- 负离子模式:适合酸性样品,如含有谷氨酸和天冬氨酸的肽类,可用氨水或三乙胺对样品碱化。pH至少高于pK值2个单位。酸性化合物很容易丢失质子,带负电荷,形成[M-H]-,m/z就是分子量要减去H。此外,还会形成[M+Cl]-,[M+HCOO]-,[M+CH3COO]-
当样本浓度特别高的时候,还会产生二聚离子,如[2M+H]+,[2M+Na]+,此时整个化合物的m/z就会增加;有时候还会形成多电荷离子,如[M+nH]n+,[M-nH]n-,这时候m/z就会减小。